Bragg's Law refers to the simple equation:
n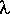 = 2d sin
= 2d sin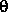
derived by the English physicists Sir W.H. Bragg and his son Sir W.L. Bragg in 1913 to explain why the cleavage faces of crystals appear to reflect X-ray beams at certain angles of incidence (theta,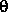 ). The variable d is the distance
between atomic layers in a crystal, and the variable lambda
). The variable d is the distance
between atomic layers in a crystal, and the variable lambda 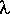 is the wavelength of the incident X-ray beam (see applet); n is an integer. For more click here.
is the wavelength of the incident X-ray beam (see applet); n is an integer. For more click here.
Courtesy: http://skuld.bmsc.washington.edu
n
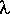 = 2d sin
= 2d sin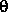
derived by the English physicists Sir W.H. Bragg and his son Sir W.L. Bragg in 1913 to explain why the cleavage faces of crystals appear to reflect X-ray beams at certain angles of incidence (theta,
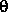 ). The variable d is the distance
between atomic layers in a crystal, and the variable lambda
). The variable d is the distance
between atomic layers in a crystal, and the variable lambda 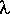 is the wavelength of the incident X-ray beam (see applet); n is an integer. For more click here.
is the wavelength of the incident X-ray beam (see applet); n is an integer. For more click here.Courtesy: http://skuld.bmsc.washington.edu


No comments:
Post a Comment
Thank you for writing to "Chemical Science"